Example Root Cause Analysis Template – Are you looking for root cause analysis templates? We have some root cause analysis, a root cause analysis template, root cause analysis examples, and more information related to it. You can also download the most suitable template for you. Let’s have a look!
About Root Cause Analysis
So, let’s talk about what root cause analysis is. There are a lot of people ask these questions. If you are one of them now it is the right time to find out about the answer. There is a factor that we cannot avoid causing non conformance and root cause needs to be abolished permanently through an improvement process. An extensive range of techniques, approaches, and tools is called as a collective term while root cause is applied to know the problems cause.
The Foundation of Root Cause Analysis
If you ask what root cause analysis is, it is an approach applied to find out the cause of an accident/incident in order to know and implement the best solution. That’s how we define it in a simple term. Usually, root cause is applied when something is haywire. But, it can also be applied during moments when everything runs smoothly. In an organization, there are three basic questions that you can see the examples of root cause, the problem solving and incident investigation. Here are those three basic questions:
- What is the incident or accident?
- Why did it happen?
- What measures will be done to prevent the problem from happening again next time?
There are two elements which root cause analysis looks to analyze. Those two things which root cause analysis looks to analyze include the problem’s symptoms and the underlying causes. You should understand it better by looking at the template of a root cause analysis. In addition, the symptom of the accident or incident usually refers to the weed above the cause(s) or the surface which are clear. On the other hand, the bottom line causes are the root that can be found below the surface or it means that the causes are hidden.
Digging underneath the problem’s surface is what root cause analysis is about. Even though instead of analyzing a single root cause, it is better to apply root cause analysis to find out a system of causes. The causes you can see below the surface are what the word ‘root’ in root cause analysis meant to. But it is quite unfortunate that the majority of the companies or organizations apply root cause analysis to find out a single cause.
It is essential for you to remember that the solution set will be limited if you only pay attention to a single cause. This is what makes you miss the best solution to manage the cause. An easy explanation of every cause of the incident is what root cause analysis has. By knowing every cause, the root provides you a chance to know various solutions to the problem. In addition, the root also gives you a chance to apply many ways to prevent problems and minimize risk. To apply root cause analysis for your organization effectively, you can follow these simple steps:
- First, the problem needs to be defined depends on its effect on the whole goals. Many people usually tend to disagree over about how to define the problem. If you define the problem depends on its effect on the goals, then you can win an agreement from the rest of the people.
- Second, create a problem’s visual map. Using the visual map, you can find out every cause of the problem.
- Finally, choose the perfect solution to minimize or prevent any negative impact that can affect the goals.
The Techniques and Approaches of Root Cause Analysis
The best way to know about the techniques and approaches of root cause analysis is analyzing at a template of the root cause. But, if you want to save time, we are going to talk about the techniques, approaches, and methodologies applied to use root cause. There are several numbers of techniques, approaches, and methodologies. But, we are going to give you five root cause approaches or techniques recommended by the Department of Energy or DOE. They are including:
- Change analysis
When the performance of a system has significantly changed, change analysis is the approach of a root cause. Change analysis looks to analyze the shift in people, equipment, information, and other things which may have affected the shift in performance.
- Causal and events factor analysis
A process which makes use of evidence collected quickly and methodically, causal and events factor analysis are used widely for many events which happen alone including a refinery explosion. In this root cause, the collective evidence is applied to set the activities’ timeline which leads to the accident. You can analyze the contributing and casual factors after the timeline has set already.
- Barrier analysis
To either prevent or detect an issue, barrier analysis a root cause technique applied to define what controls are in place.
- Risk tree and management oversight analysis
To see what happened and determine why an issue happened, risk tree and management oversight analysis is the approach used in root cause. This approach includes the use of a tree diagram. You can have a better understanding of risk tree analysis and management oversight by analyzing the root cause or examples.
- Problem-solving
This approach of root cause includes the use of four various analysis techniques. These are the four techniques used by the Kepner-Tregoe. The problem solving and decision-making approach is including:
- Solution analysis
- Potential problem analysis
- Situation analysis
- Problem analysis
So, those are five approaches and techniques used for root cause analysis. The approaches and techniques written above can be overlapped so you might need to take a look at the examples of root cause to know which approach is the best one for you. Now, since we have talked about the root cause it is the time for you to apply it in real life. Good luck!
Importance of Root Cause Analysis
Every organization encounters problems. However, it is how these issues are dealt with that truly counts. One of the useful problem-solving methods is (RCA). But why is it so important?
It is a systematic method developed to uncover the real reason for a problem rather than merely addressing its symptoms. By finding the underlying or “root” cause, we can control the situation from recurring. It is crucial for continuous improvement and growth in any organization.
When we face a problem, it’s often tempting to jump to quick answers to get things back on track. However, these solutions usually only address the signs of the issue rather than the real reason. Consequently, the issue may reoccur, leading to repeated disruption and wasted resources.
By using RCA, organizations can determine and fix the root causes of issues, leading to long-term solutions that prevent issues from recurring. These outcomes in improved productivity, better quality, increased safety, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
In addition, RCA fosters a proactive culture of learning and continuous improvement within the organization. It encourages teams to dig deeper into problems and learn more about their plans and procedures. This knowledge helps them make better decisions and prevent issues before they arise.
How to Conduct a Root Cause Analysis: Step-by-Step Guide
It can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. Here’s a simple, step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Determine the Issue. Explain the issue. Contain when it occurs, its effect, and any relevant details.
Step 2: Gather Data. Collect all data connected to the issue. It could include documentation, records, and first-hand accounts from people involved.
Step 3: Identify Possible Causes List all potential causes of the problem. Brainstorm with your team, and don’t leave any stone unturned.
Step 4: Determine the Root Cause. Investigate the potential causes to identify which one(s) are the root cause of the problem. It could involve further data analysis, experimentation, or simulations.
Step 5: Develop and Implement Solutions Create a plan to address the root cause and prevent recurring problems. It may involve changes to processes, systems, or behaviors. Implement the plan and watch its significance.
Step 6: Monitor the Outcome After executing the resolution, monitor the situation to confirm the problem has been fully resolved and doesn’t reoccur.
Root Cause Analysis is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the issue and your community’s needs, you might need to adapt these steps or use specific RCA techniques like 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, or Fault Tree Analysis. The key is to remain focused on uncovering the true cause of the problem rather than settling for quick fixes that only deal with the symptoms.
To sum up, Root Cause Analysis is an essential tool for any organization seeking to enhance operations, control future problems, and foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. By digging deeper into problems and addressing their root causes, we can create more effective and sustainable solutions for the future.
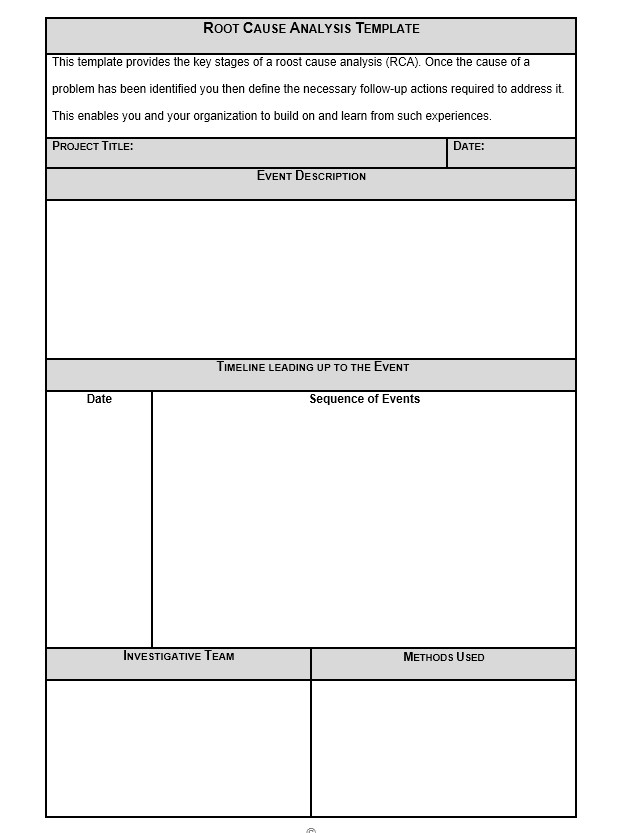
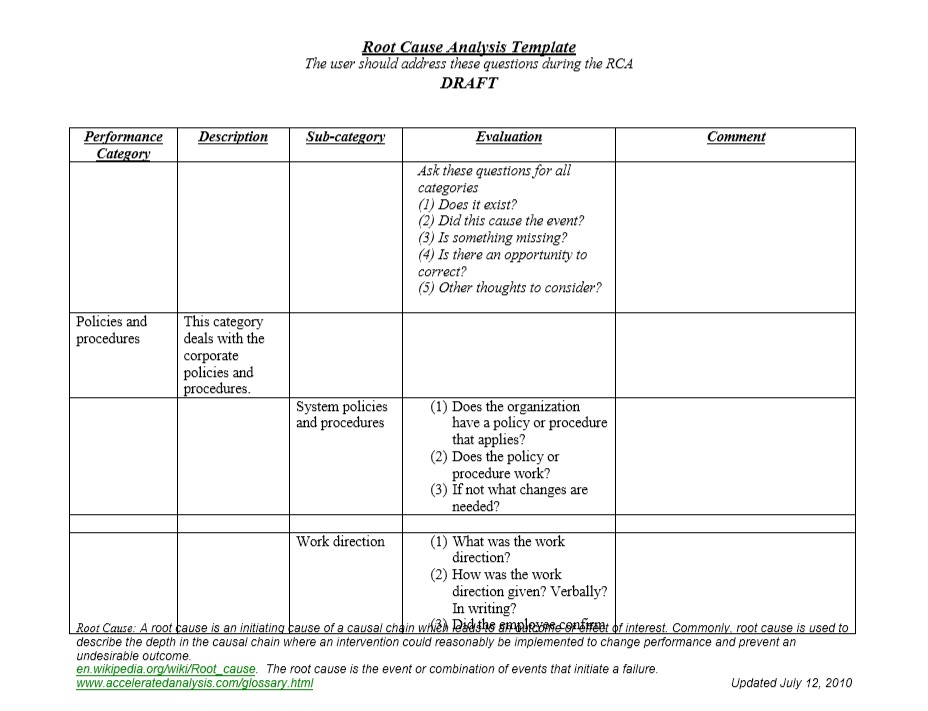
Root Cause Analysis Templates
These templates provide a structured format where you can input data and organize information, making the process more manageable. Here are some types of Root Cause Analysis templates you can use:
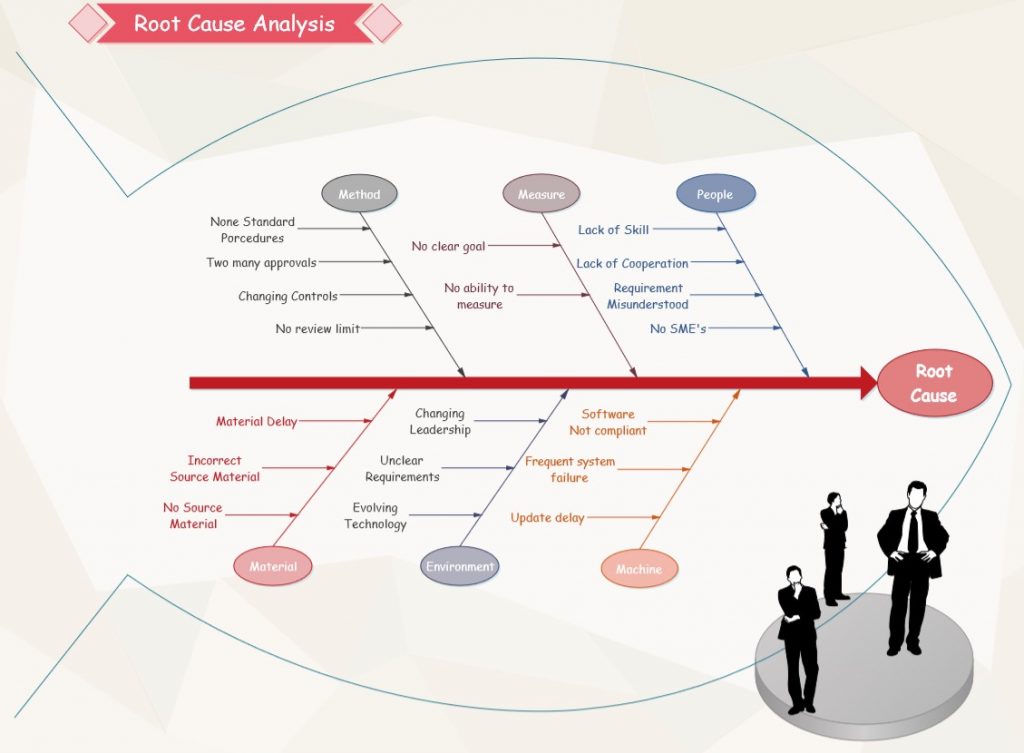
Fishbone Root Cause Analysis Template
This template aids in categorizing possible reasons for issues into branches, delivering a graphic illustration.
Simple Root Cause Analysis Template
A straightforward and minimalist template designed to assist users in quickly recognizing and documenting the issue without extensive points.
Incident Root Cause Analysis Template
this template helps users dissect unexpected events or disruptions to pinpoint their fundamental cause, aiding in prevention and mitigation.
Human Error Root Cause Analysis Template
Specifically designed to delve into mistakes or oversights made by individuals, facilitating an understanding of why the error occurred and how to prevent it.
8D Root Cause Analysis
An 8-discipline methodology used primarily for problem-solving. It includes steps from recognizing the issue to executing corrective measures and verifying their long-term effectiveness. Frequently employed in manufacturing and production industries, the 8D approach emphasizes team collaboration.
Root Cause Analysis 6 Steps
A structured six-step process that typically involves:
- Problem identification
- Problem description
- Establishing a team
- Root cause identification
- Developing and implementing corrective actions
- Reviewing the effectiveness of those actions. This method is known for its simplicity and adaptability across different industries.
Root Cause Analysis Template PPT
It is designed to showcase findings, insights, and recommendations from an RCA, ideal for group discussions or presentations.
Root Cause Analysis Template NHS
A template tailored for the National Health Service (UK) to identify and address root causes within healthcare scenarios, adhering to their specific guidelines and standards.
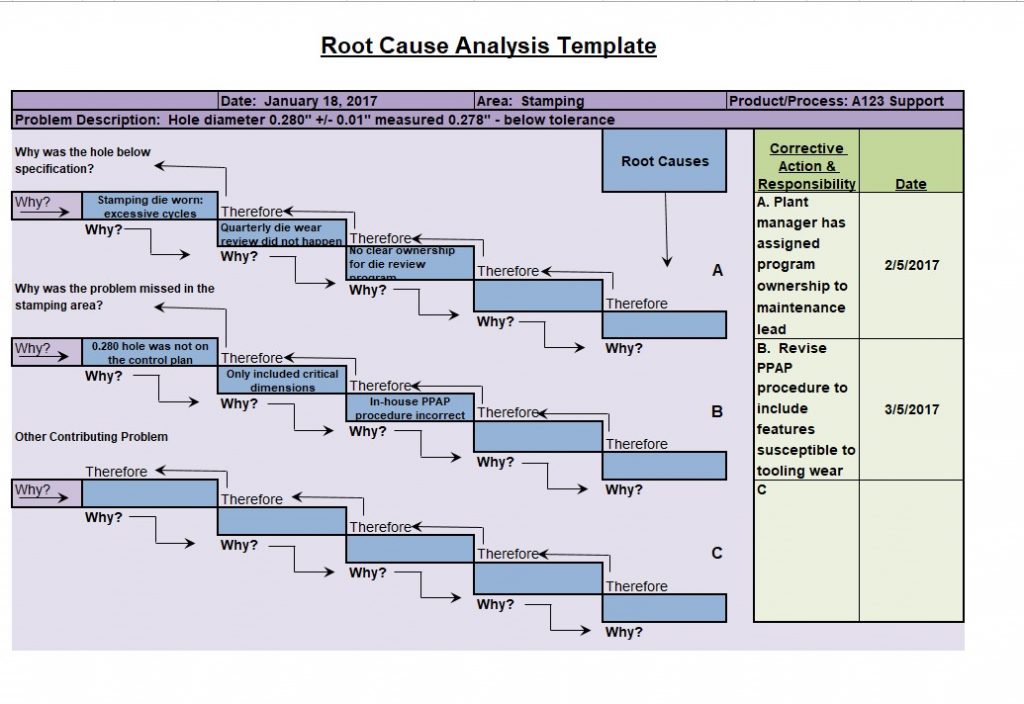
Root Cause Analysis Template 5 Whys
A template that utilizes the “5 Whys” methodology, a technique that repeatedly asks “why” to drill down into the root cause of a problem.
Root Cause Analysis Template Free
A no-cost template for users to guide them in the RCA process, usually downloadable from online resources.
A standardized composition that guides individuals or teams in determining the fundamental reason for a problem or issue.
Root Cause Analysis Template Word
guides users through documenting and diagnosing problems.
The 5 Whys Template
This template is quite straightforward. It consists of a series of boxes or lines where you can write down each ‘why’ question and its answer, leading to the root cause. The simplicity of this template makes it easy to use, even for beginners.
Fishbone Diagram Template
A Fishbone Diagram template can come in handy when considering many potential causes. This template typically includes a blank ‘fish’ with categories as ‘bones.’ You fill in the potential causes under each category. Some templates include common categories for different industries or problem types.
Fault Tree Analysis Template
FTA templates are more complex as they need to accommodate various logic gates and potential sequences of events. However, once you understand how they work, these templates can be powerful tools for dissecting complex problems.
While you can create these templates, plenty are available online for free download. These templates can save time and ensure you’re not overlooking potential causes.
Root Cause Analysis Pdf
A digital format that provides detailed insights or guidelines on performing an investigation, ideal for sharing and distribution.
Root Cause Analysis Healthcare
A specialized approach to RCA that focuses on diagnosing and addressing underlying causes of issues within healthcare settings, enhancing patient safety and care quality.
Root Cause Analysis Template Excel
This Is designed in Microsoft Excel to facilitate the systematic recording and analysis, usually including interactive features.
Tips for Conducting a Root Cause Analysis
Carrying out a **Root Cause Analysis (RCA)** requires a systematic approach, the right group of people, and a focus on the real issue. Here are some practical tips to guide you through the process:
- Be Systematic
An effective RCA is a smooth process. It needs to be systematic and step-by-step. Start by defining the problem accurately, then collect data, identify potential causes, find the root cause, and develop corrective actions. Being systematic ensures that every important detail is noticed.
- Involve the Right People
The people involved in the RCA should understand the process or system and have a direct connection to the problem. It can include staff who work with the process or experts in the area. You tap into a wealth of knowledge and experience by involving the right people.
- Focus on the Root Cause
It’s easy to get sidetracked by symptoms of the problem or immediate causes. However, an RCA aims to uncover the root cause—the underlying issue that led to the problem. Ask “why” until you can’t ask “why” anymore.
- Use Visual Tools
Visual tools like Fishbone Diagrams or Fault Tree Analysis can help lay out potential causes and see how they connect. These tools can also be beneficial in communicating the findings of the RCA to others.
- Validate Your Root Cause
Once you think you’ve identified the root cause, validate it. It could involve conducting tests, reviewing data, or confirming with experts. Validation helps ensure that you’ve got the right cause and that your corrective actions will be effective.
- Develop and Implement Corrective Actions
Identifying the root cause isn’t the end of an RCA. You should also develop corrective actions to address the root cause and then implement these actions. Afterward, monitor to ensure that the actions prevent recurring problems.
Parts of a Root Cause Analysis
A **Root Cause Analysis (RCA)** is a structured method to understand the core reason behind a particular problem or fault. To conduct it effectively, one must ensure that they go through certain essential elements. Here’s a closer look at the parts of an RCA:
Problem Definition
- Clarity: Start by clearly defining the problem. A vague problem statement will lead to unclear results. Be specific about what occurred, when it happened, and the extent of its impact.
- Data Collection: Gather all relevant data about the problem. It could include the time the problem was first noticed, the conditions under which it appeared and any deviations from the norm.
Cause Identification
- Brainstorming: Assemble a team of individuals familiar with the process or system and brainstorm all possible causes of the problem.
- Use RCA Tools: Tools such as the Fishbone Diagram or the 5 Whys technique can help visually organize potential causes and dig deeper into the issue’s root.
Cause Evaluation
- Investigation: Dive deep into each identified cause to determine if it contributed to the problem. Some causes might be more symptoms rather than root causes.
- Validation: Validate each cause by cross-checking with data, talking to experts, or experimenting. It ensures that you focus on actual causes, not just perceived ones.
Solution Implementation
- Development of Solutions: Once the root cause has been identified, brainstorm potential solutions that would address this cause effectively. It’s important to come up with solutions that are practical and feasible.
- Action Plan: Develop a clear plan for implementing the chosen solution. This plan should outline who does what, by when, and with what resources.
- Monitoring: After implementing the solution, monitor the situation to ensure that the problem doesn’t recur and verify the effectiveness of the corrective action.
Documentation and Review
- Record-Keeping: Document every step of your RCA process. It provides a reference for the future and ensures transparency in the process.
- Feedback Loop: Review the RCA process after some time to identify any areas of improvement. It can help in refining the process for future use.
Giving importance to each component will ensure that the underlying issue is accurately identified and appropriately addressed.
Examples of Root Cause Analysis
Let’s delve into some real-world examples of RCA in action:
1. Healthcare: Patient Falls in Hospitals
- Problem: A hospital noticed increased patient falls in the past six months.
- RCA Technique Used: Fishbone Diagram
- Findings: Multiple factors were identified: inadequate lighting in hallways, inconsistent use of non-slip socks, insufficient staff training on patient transfer techniques, and lack of regular checks on high-risk patients.
- Outcome: The hospital made improvements such as enhancing hallway lighting, mandatory use of non-slip socks, specialized training for staff, and a revised protocol for checking on high-risk patients. Fall incidents significantly decreased afterward.
2. Manufacturing: Defective Products
- Problem: A toy manufacturer found that one of its toy models had a higher defect rate than usual.
- RCA Technique Used: 5 Whys
- Findings: By asking “why” repeatedly, it was discovered that a particular machine was misaligned, leading to defects.
- Outcome: Regular maintenance and alignment checks for the machinery were implemented, drastically reducing defects for the affected toy model.
3. Information Technology: Server Downtime
- Problem: An IT company experienced frequent unplanned server downtimes.
- RCA Technique Used: Fault Tree Analysis
- Findings: The main contributors were outdated server firmware, lack of redundancy in power supplies, and inadequate cooling in the server room.
- Outcome: The company updated all server firmware, introduced power supply redundancies, and improved the server room’s cooling system. Server downtimes were significantly reduced.
4. Aviation: Near-miss on the Runway
- Problem: Two planes almost collided on the runway.
- RCA Technique Used: Event and Causal Factor Analysis
- Findings: Miscommunication between the air traffic controller and the pilots, outdated airport ground radar systems, and pilot fatigue were determined to be the main causes.
- Outcome: Air traffic control protocols were revised, the airport updated its radar systems, and stricter regulations were set for pilot work hours, ensuring such incidents were less likely to occur.
These examples highlight the effectiveness of RCA in diverse sectors. The key takeaway is identifying the root cause and implementing solutions that prevent future recurrences of the problem.
Effective RCA ensures processes are optimized, risks are minimized, and overall productivity and safety are enhanced.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced and complex operational environments, problems and setbacks are inevitable. However, how we approach, dissect, and learn from these challenges makes a difference. **Root Cause Analysis (RCA)** stands as a beacon in this journey of continuous improvement.
RCA isn’t just about identifying what went wrong; it’s a deep dive into understanding **why** something happened. By moving past the immediate symptoms and delving into the root cause, organizations can craft effective and enduring solutions. This proactive approach doesn’t just remedy the current problem but fortifies processes against future issues.
Through the techniques like the 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram, and Fault Tree Analysis, the convenience brought by RCA templates, and the best practices shared, we’ve seen how multifaceted and dynamic RCA can be. But more than the techniques and tools, the mindset of digging deeper and striving for genuine understanding is the real game-changer.
In a world that often rewards quick fixes, RCA challenges us to think long-term, prioritize sustainable solutions, and embrace a culture of continual learning and improvement. By doing so, we address the challenges at hand and set ourselves up for greater success and resilience in the future.
FAQs
What exactly is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Answer: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach used to identify the fundamental cause of a problem or failure. By determining the root cause, organizations can implement solutions that prevent similar problems from recurring in the future.
Why can’t we fix the immediate problem instead of doing RCA?
Answer: While fixing the immediate problem provides a temporary solution, it doesn’t prevent the issue from happening again. RCA delves deeper to uncover the underlying cause, allowing for long-term solutions that prevent recurrence.
How long does a typical RCA take?
Answer: The duration of an RCA can vary widely depending on the complexity of the problem, the method used, and the available resources. Simple issues may be resolved within hours, while complex ones might take weeks or longer.
Can RCA be applied to any problem or industry?
Answer: Yes, RCA is versatile and can be adapted to various problems across different industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, IT, aviation, and more.
Is RCA always done after a problem has occurred?
Answer: While RCA is commonly initiated after a notable incident or failure, it can also be used proactively to identify potential issues and address them before they escalate.
Does RCA always identify a single root cause?
Answer: Not always. Sometimes, there might be multiple root causes that contribute to a problem. RCA aims to identify all significant underlying causes, whether singular or multiple.
How is RCA different from regular problem-solving?
Answer: While general problem-solving often targets symptoms or immediate causes, RCA goes deeper. It seeks to uncover the primary cause(s) behind a problem, ensuring a more effective and lasting solution.
Is using RCA templates effective?
Answer: Yes, using RCA templates can streamline the process, ensure all necessary steps are followed, and provide consistency in the analysis. Templates are particularly beneficial for organizations new to RCA or those seeking to standardize their approach.

The content creator team at calipsotree.com is dedicated to making topics accessible to everyone, with over 9 years of experience in writing and breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand articles that answer readers’ financial questions.