A vaccination schedule has the timing of all doses guided from birth throughout life. Many aspects, including the kind of vaccine, the age, health disease, and immune level of the recipient, determine the specific vaccines and their management schedule.
Vaccination schedules play a crucial role in preventing diseases and maintaining public health. They are designed to protect individuals and the broader community from severe infectious diseases before they have a chance to take hold. By following a vaccination schedule, individuals can ensure they are protected from certain diseases at the right time for maximum effectiveness.
Vaccines, such as making antibodies to fight the disease, stimulate our immune system to respond. If the individual is later revealed to that disease, their resistant system can quickly combat it. Therefore, following a vaccination schedule is critical to disease prevention and overall health maintenance.
Knowing the Most Common Schedule Vaccination
MMR Vaccine and the schedule
HPV Vaccine and the schedule
Vaccination Schedule
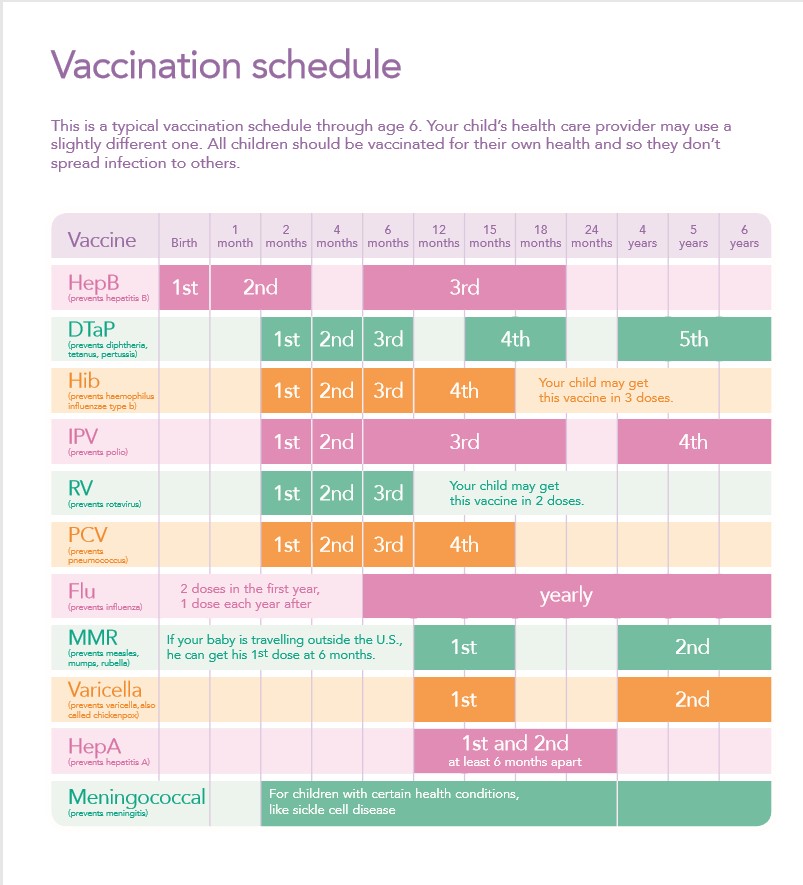
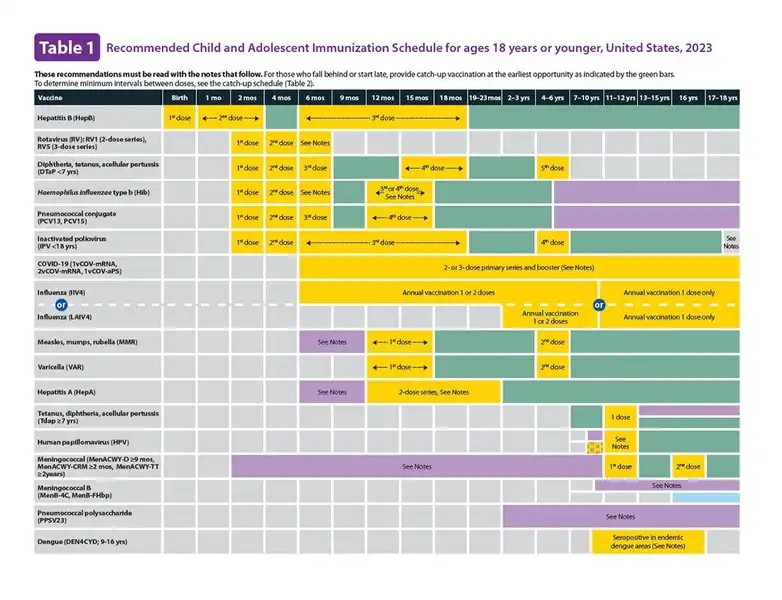
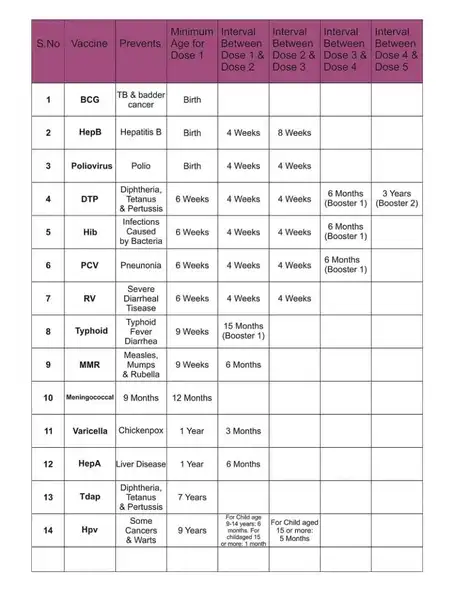
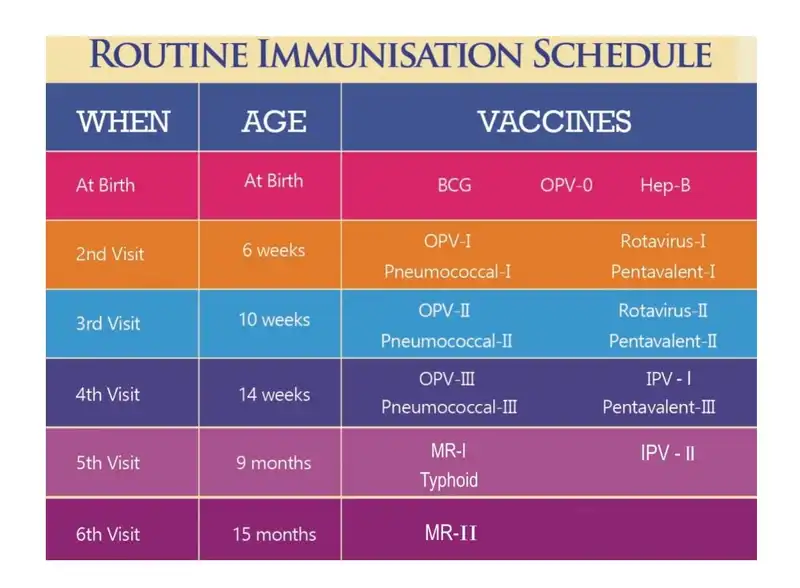
Importance of Vaccination Schedule
The importance cannot be overstated. It is a critical tool in infection prevention and public health maintenance for several reasons:
- Timely Protection: It protects individuals when they are most vulnerable to certain diseases. For example, many vaccines are given in early childhood because the risk of contracting the disease is highest.
- Herd Immunity: Vaccination schedules contribute to herd immunity, a form of avoiding protection from infectious conditions that happens when a big person has evolved immune to disease. This protects individuals who are not immune or cannot receive vaccines.
- Prevention of Outbreaks: By ensuring that a large portion of the population is vaccinated against a particular disease, vaccination schedules help prevent outbreaks of that disease. This is particularly important for highly contagious diseases.
- Cost-Effective: Preventing disease through vaccination is usually much less expensive and stressful than treating an illness. Vaccination schedules, therefore, are a cost-effective way of managing public health.
- Eradication of Diseases: Widespread vaccination following a specific schedule can lead to the complete eradication of diseases. A prime example of this is the eradication of smallpox.
A vaccination schedule is a key component of individual and public health, helping to prevent the spread of infectious diseases, reduce the impact of such diseases on communities, and even eradicate certain diseases.
Importance of Vaccination for Women
Vaccinations are essential for everyone, but some are vital for women due to specific health hazards. The HPV vaccine is one such example. It helps avert cervical cancer, which HPV primarily drives.
The vaccine also covers other HPV-related cancers, such as vaginal, vulvar, and throat. Additionally, it controls genital warts, a typical HPV symptom.
By vaccinating, women safeguard their health and contribute to community protection by reducing the virus’s prevalence. Hence, women must follow recommended vaccination schedules.
Importance of Vaccination for Children
Vaccination plays a crucial role in saving children from severe infections. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to respond and build immunity by submitting small, safe bacteria into the body. Here’s why it’s particularly important to start vaccinations at a young age:
Building immunity Early: Children are exposed to potential disease-causing agents every day. Vaccinating them at a young age helps build their immunity early, protecting them from conditions that could be serious or even fatal.
Preventing Outbreaks: Vaccination doesn’t just protect the individual who accepts the vaccine. It also helps prevent attacks of infections in the community.
When an increased rate of the population is immunized, it’s harder for a condition to apply. This protects those who cannot be vaccinated, such as newborns or those with certain medical conditions.
Long-term Protection: Many vaccines provide long-term or even lifelong protection against diseases. Vaccinating children allows them to grow into adults covered against specific conditions.
Safe and Effective: Vaccines are tested for safety and effectiveness before approval. They’re a safe method to save children from infections.
Saving Time and Money: vaccines often result in prolonged hospital stays and long-term health problems that can be costly. Vaccination, on the other, is a cost-effective method of controlling infections.
Starting vaccinations at a young age is crucial to building a child’s immunity and protecting them from serious diseases. Parents must follow the recommended vaccination schedule to protect their children.
Vaccination Laws
Here’s a brief overview of how some countries approach vaccination laws:
Mandatory Vaccination Laws:
It means that certain vaccines are required for everyone, often with a particular focus on children. For example, in Australia, certain benefits are tied to a child’s vaccination status under a policy called “No Jab, No Pay.” In Italy, children must receive a series of mandatory immunizations before they can be enrolled in school.
Recommended but Not Required:
Vaccines are strongly recommended but not legally required in other countries. In the UK, the government recommends a series of vaccines for children and adults, but there are no penalties for choosing not to vaccinate.
Vaccine Exemptions:
There are often medical, religious, or philosophical exemptions, even in countries. However, the ease of obtaining these exemptions varies. In some US states, for example, non-medical exemptions have been eliminated in response to measles outbreaks.
Vaccination and Travel:
Some countries require proof of vaccination against certain diseases for entry. The most common example is the yellow fever vaccine, which is required for travel to certain parts of Africa and South America.
COVID-19 Vaccination Laws:
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought new attention to vaccination laws. Some countries have made COVID-19 vaccination for certain groups, such as healthcare workers or people over a certain age.
Vaccination laws are a complex issue that balances public health needs with individual rights. They are a key tool in the global effort to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Risks of Not Following Vaccination Schedules
It can pose risks and consequences for individuals and the wider community. Here are some key points to consider:
Increased Susceptibility to Diseases
Vaccines prepare the body’s immune system to fight off specific diseases. If a person does not receive a vaccine, they remain susceptible to the disease it protects against. This can lead to serious illness or even death in the case of severe diseases.
Risk of Outbreaks
Vaccination isn’t just about protecting individuals—it’s also about protecting communities. When a high percentage of a population is vaccinated against a particular disease, it becomes harder for it to spread. This phenomenon is known as herd immunity. Not following vaccination schedules can lower the community’s overall immunity level, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
Delayed Protection
Vaccination schedules are designed to provide protection when people are most vulnerable. For example, many vaccines are given in early childhood, when the risk of disease complications can be particularly high. Delaying vaccines can leave children unprotected when they need it most.
Ineffective Vaccination
Some vaccines need to be given in multiple doses to be effective. If the schedule is not followed, and doses are missed or given too far apart, the vaccine may not provide full protection.
Risk to Others
It can also pose a risk to people who cannot be vaccinated, such as those with certain medical conditions, allergies, or very young infants. These individuals rely on herd immunity for protection.
Following schedules is crucial for individual health, public health, and preventing infectious diseases.
Conclusion
Vaccination schedules play a pivotal role in safeguarding individual and public health. Healthcare professionals meticulously design them to provide immunity against various diseases at appropriate times.
Starting from infancy, these schedules protect us when we are most vulnerable and continue to shield us throughout our lives. They are particularly crucial for women due to certain gender-specific diseases like HPV and for children who are building their immunity.
However, the effectiveness of vaccination schedules is about more than individual protection. It’s also about our communities’ collective immunity, often called herd immunity. This collective protection can significantly reduce the risk of disease outbreaks, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated for medical reasons.
Despite the clear benefits, it’s important to be aware of the legal aspects of vaccination, which can vary across different countries. Some have mandatory vaccination laws, while others leave it to personal choice.
The risks of not adhering to vaccination schedules are significant. They include increased susceptibility to diseases, risk of outbreaks, delayed protection, ineffective vaccination, and potential harm to others.
FAQs
Why are vaccination schedules important?
They are important because they provide each vaccine’s most effective timing and sequence.
Can I delay or skip certain vaccines on the schedule?
It is not advisable to delay or skip vaccines. The schedule is designed to provide protection when individuals are most vulnerable. Delaying or skipping vaccines can leave individuals at risk of contracting preventable diseases.
What happens if we miss a vaccine on the schedule?
If a vaccine is missed, it’s important to reschedule as soon as possible. Most providers have catch-up schedules to ensure individuals can still receive the vaccine and be protected.
Are there side effects to vaccines?
Like any medication, vaccines can have side effects. However, most are mild and temporary. Serious side effects are rare. Preventing serious illness and complications far outweighs the potential risks of side effects.
Are vaccination schedules the same in every country?
No, vaccination schedules can vary from country to country. They are designed based on the prevalence of diseases, risk factors, and healthcare practices in each country.
Why are some vaccines mandatory?
They are made mandatory by law in certain countries to ensure widespread immunity and prevent outbreaks of diseases. This is particularly important for highly contagious diseases.
Can adults follow vaccination schedules?
Yes, adults can and should follow vaccination schedules. Vaccines are recommended for adults with specific health conditions, occupations, or lifestyle factors.
Resources for More Information on Vaccination Schedules
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): They provide information on vaccination schedules for all age groups, from infants to adults. They also provide resources on vaccine safety, effectiveness, and the science behind vaccines. Visit their website https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/index.html.
World Health Organization (WHO) provides global vaccination schedules and guidelines. They also offer resources on vaccine-preventable diseases and the latest research on vaccines. Visit their website https://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/en/.
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): The AAP provides resources on childhood vaccination schedules and the importance of vaccines in preventing diseases. Visit their website https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/immunizations/Pages/Immunizations-home.aspx.
National Health Service (NHS): The NHS provides information on the UK’s vaccination schedule and resources on the importance of vaccines. Visit their website https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vaccinations/.
Immunize Canada: provides information on Canada’s vaccination schedules and resources on vaccine safety and effectiveness. Visit their website https://immunize.ca/.
Remember, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider for personalized vaccination advice.

The content creator team at calipsotree.com is dedicated to making topics accessible to everyone, with over 9 years of experience in writing and breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand articles that answer readers’ financial questions.








