Free Sample Incident Report Template – Any incident and accident in both minor and major categories must be recorded, reported, and written into an incident report to ensure that the institution, organization, or company has the latest incident or accident prevention measures and the risk of recurrence of a similar incident can be minimized. Do students, employees, or workers have to report any incidents? What kind of incident must be reported? Why should an incident report be made? How do you make an incident report?
Incident reporting is critical to any organization, institution, or company’s security and risk control system. It is a systematic method for documenting unforeseen events or accidents that could cause harm or disrupt normal operations. The incident volume cannot be overstated, as it is pivotal in maintaining a safe and secure environment.
Importance of Incident Reporting
One of the primary reasons it is essential is that it aids in updating safety measures. When an incident is reported, it delivers useful insight into where and how safety measures may have failed or been inadequate. This information authorizes institutions to review and revise their current safety protocols, making necessary improvements to deter similar incidents from arising in the end. For instance, if an employee slips and falls due to a wet floor, the incident report could lead to more useful signage during cleaning or even a review of cleaning schedules to minimize risk.
Incident reporting helps minimize the risk of future similar incidents. Institutions can recognize practices or trends in security breaches or accidents by recording. This data can then be interpreted to predict and control future incidents, enhancing safety. For example, the association can analyze and manage the underlying problem if multiple incidents appear in a particular area or during a typical operation.
Incident reporting also advances a culture of security within the association. When workers are urged to report incidents, it sends a clear notice that their security is a priority. It can boost confidence and encourage a more engaged and productive workforce. Furthermore, it allows institutions to comply with lawful and regulatory needs, as many jurisdictions require reporting and investigating.
Incident reporting is required for improving safety and controlling accidents in any organizational setting. By documenting and learning from each incident, organizations can continually improve their safety measures, ultimately creating a safer and more secure environment.
Types of Incidents to Report
Understanding what constitutes an incident that requires being informed is crucial for maintaining a safe and secure environment.
The definition of an incident can vary depending on the context and the organization, but generally, it refers to any event that disrupts normal operations or could potentially cause harm.
Here are some types of incidents that typically need to be reported:
- Workplace Accidents: Any accident that occurs in the workplace, regardless of severity, should be noted. It could range from minor incidents like slips, trips, and falls to heavy machinery or tools accidents.
- Near Misses: It is an incident where no effects were injured, and no personal injury was supported but where, provided a small change in time or place, harm or injury easily could have happened.
- Health and Safety Hazards: Any condition threatening health and security should be registered. It could include a faulty ladder, a spill that needs to be cleaned up, or inadequate personal protective gear.
- Security Incidents: Any security breach, such as theft, vandalism, or unauthorized access to restricted areas, should be reported.
- Incidents Involving Clients or Customers: Any incident that affects or involves a client or customer, such as a customer injury or a complaint about a serious issue, should be reported.
- Environmental Incidents: Any incident that could harm the environment, such as a chemical spill or improper disposal of hazardous waste, should be reported.
- Violence or Harassment: Any incident involving violence, harassment, or inappropriate behavior in the workplace should be reported, regardless of who is involved.
When in doubt, it’s better to report an incident. Even minor incidents can provide valuable information that can help prevent more serious incidents in the future.
The Role in Workplace Safety
It plays a pivotal role in maintaining and enhancing workplace safety. It is a critical tool for institutions to assess their security performance, identify possible hazards, and implement preventative measures. Here’s how incident reporting contributes to workplace safety:
- Recording and Documenting Incidents: It provide a detailed record of what happened, when it happened, who was involved, and what actions were taken. This documentation is required to comprehend the incident’s circumstances and can be used for future reference or in legal proceedings.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: Regular incident reporting allows organizations to identify trends and patterns in accidents or near misses. For example, if a particular type of accident keeps occurring, it might indicate a larger systemic issue that needs to be addressed.
- Preventing Future Incidents: By analyzing, organizations can identify the root causes and take steps to prevent similar incidents. It could involve changing workplace procedures, providing additional training, or implementing new safety measures.
- Promoting a Safety Culture: It promotes a safety culture within the organization. It encourages employees to be vigilant about safety and to take responsibility for reporting any incidents or hazards they observe.
- Compliance with Regulations: In many industries, incident reporting is not just a good practice but a legal requirement. Regular reporting ensures that organizations comply with health and safety regulations and can provide evidence of compliance if required.
- Enhancing Communication: It enhance communication about safety issues within the organization. They ensure that information about incidents is shared with relevant parties, including management, employees, and health and safety representatives.
Incident reporting is a cornerstone of effective workplace safety. It provides useful insights into security performance, helps to deter future incidents, and fosters a culture of security and responsibility.
Barriers to Effective
While incident reporting is a crucial aspect of maintaining workplace safety, several barriers can hinder its effectiveness.
Understanding these barriers can help organizations address them and foster a more open and effective incident-reporting culture. Here are some common barriers to effective incident reporting:
- Fear of Repercussions: One of the most significant barriers to incident reporting is the fear of repercussions. Employees may worry that reporting an incident could lead to disciplinary action, job loss, or damage to their reputation. To overcome this barrier, organizations should foster a culture of safety where employees feel safe to report incidents without fear of retaliation.
- Perception of Incident Severity: Employees may not report incidents that they perceive as minor or insignificant. They might think that only major incidents need to be reported. However, even minor incidents can provide valuable insights and help prevent more serious incidents in the future. Organizations should encourage employees to report all incidents, regardless of their severity.
- Lack of Awareness: Employees may only report incidents if they know the procedures. They might need to learn what constitutes an incident, who to report to, or how to fill out an incident report. Regular training and clear communication help ensure that all employees understand the importance of incident reporting and how to do it.
- Time Constraints: Employees may need more time to complete incident reports in a busy work environment. They might see it as additional paperwork that detracts from their primary duties. Organizations can strive to make the reporting process as simple and efficient as possible to address this barrier.
- Desire to Maintain a Clean Record: Some organizations or employees may refrain from reporting incidents to maintain a clean safety record. However, this approach can lead to unaddressed safety issues and potentially more serious incidents in the future. Organizations must emphasize that a clean record is less important than learning from incidents to improve safety.
By understanding and addressing these barriers, organizations can enhance their incident reporting practices and create a safer work environment for all employees.
Steps to Write an Incident Report
It allows organizations to comprehend the incident’s circumstances and take reasonable steps to avert comparable occurrences. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an effective incident report:
- Immediate Response: The first step after an incident is to confirm everyone’s security and provide necessary medical attention. Once the immediate needs are addressed, the incident should be notified to the relevant person or department within the organization.
- Collect Facts: Gather all the points about the occurrence. It could contain points about what occurred, where and when, who was applied, and any potential witnesses. Collecting this data as soon as possible while the details are still fresh is important.
- Determine the Chronology: Demonstrate a clear timeline of experiences showing up to, during, and after the happening. It can assist in determining any aspects that may have contributed to the incident.
- Incident Analysis: Examine the experience to comprehend why it occurred. It could involve whether safety procedures were observed, the tools were functioning correctly, or environmental factors played a role. The goal is to identify the incident’s root cause to prevent similar incidents in the future.
- Determine Corrective Actions: Based on the analysis, determine what corrective actions must be taken. It could include procedure changes, additional training, equipment upgrades, or other measures to improve safety.
- Write the Report: Finally, compile all this information into a clear, concise, factual incident report. The report should include all the incident details, the analysis findings, and the proposed corrective actions. It should be objective, avoiding blame or personal opinions.
- Review and Follow-Up: After the report is written, it should be reviewed by the appropriate parties, such as supervisors or safety officers. They can provide feedback, approve the proposed actions, and ensure they are implemented. Following up on the report is important to ensure that the corrective actions have effectively prevented similar incidents.
Organizations can ensure that their incident reports are thorough, accurate, and effective in improving workplace safety.
Sample incident report template
Making an report involves important steps, including immediate response, collecting facts, determining the chronology, incident analysis, and determining corrective actions. If you are not sure about how to write an report, you can download the incident report template here.
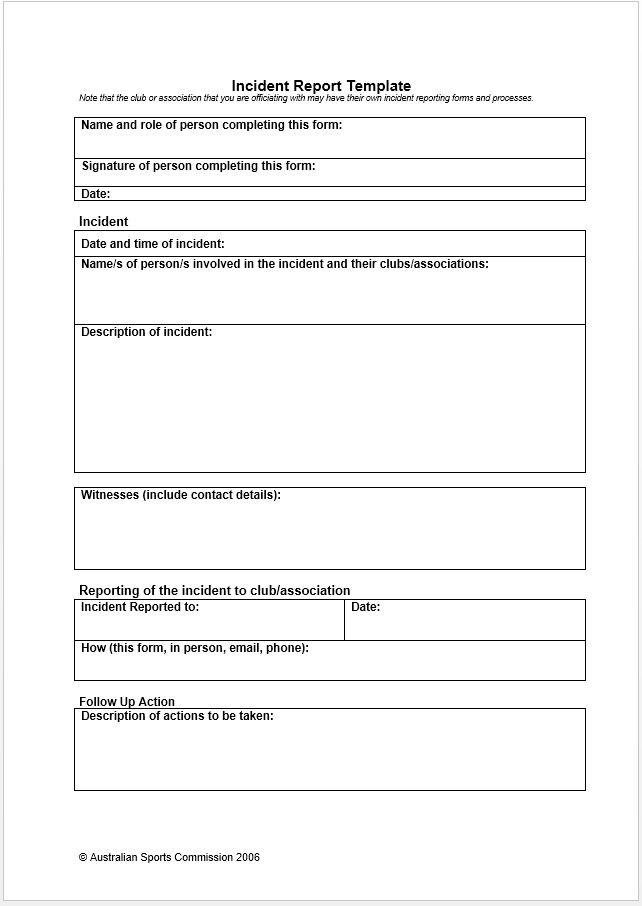

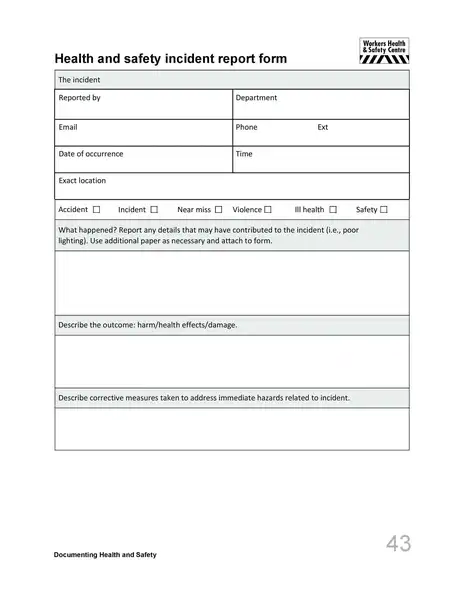
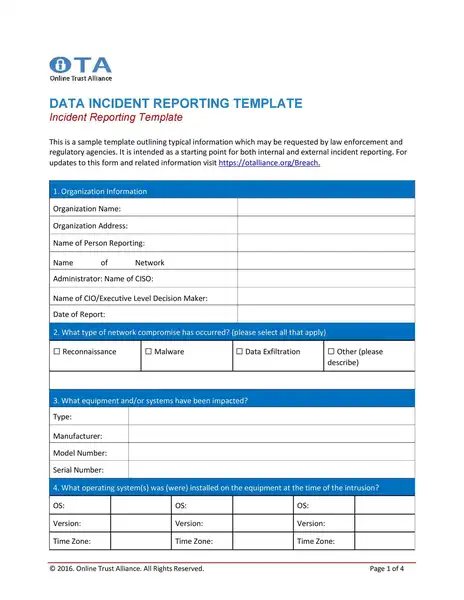
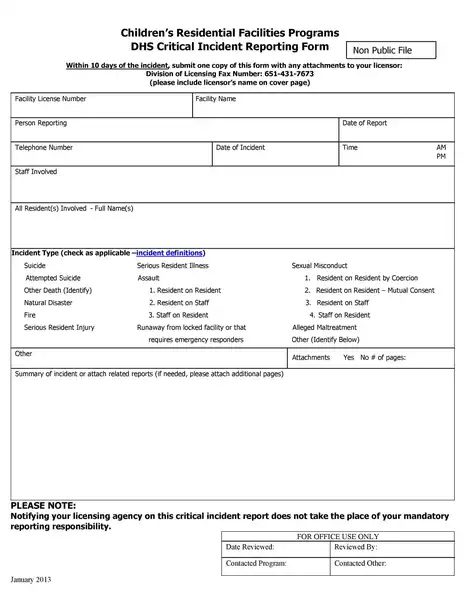

Incident Report Templates
These templates are created to capture all the necessary information in a structured and organized manner. Here’s how these templates can help you:
- Structure: It is a predefined structure, ensuring that all critical information is included. It typically has sections for details about the happening, someone interested, the timeline of events, the study of the happening, and the corrective actions proposed.
- Consistency: It ensures consistency across all incident reports within an organization. This consistency creates it more comfortable to review and compare reports, identify trends, and track improvements over time.
- Efficiency: Templates keep period and step by delivering a design you can fast fill out. Instead of stressing about the layout or what information to include, you can concentrate on accurately representing the incident and identifying effective corrective actions.
- Compliance: Many templates are prepared to meet the reporting requirements of regulatory bodies. Such a template can help ensure your organization complies with relevant laws or regulations.
- Training: Templates can also be a training tool for staff members new to incident reporting. By providing a clear example of what an incident report should look like, templates can help new staff understand what information they need to include.
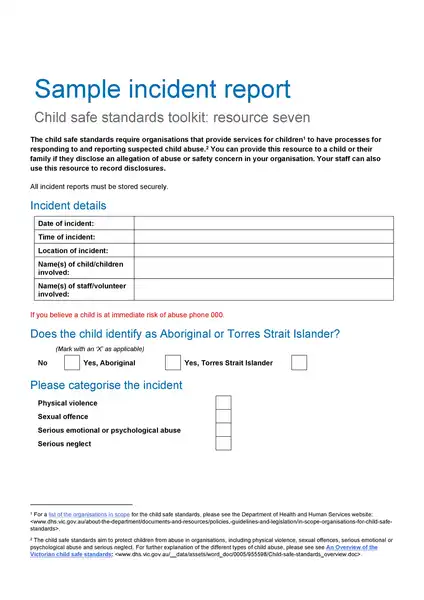
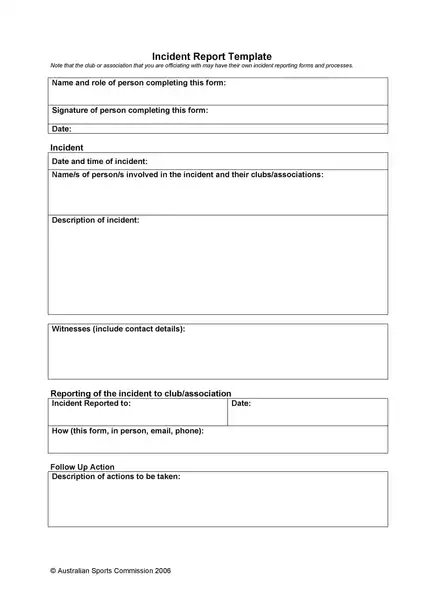


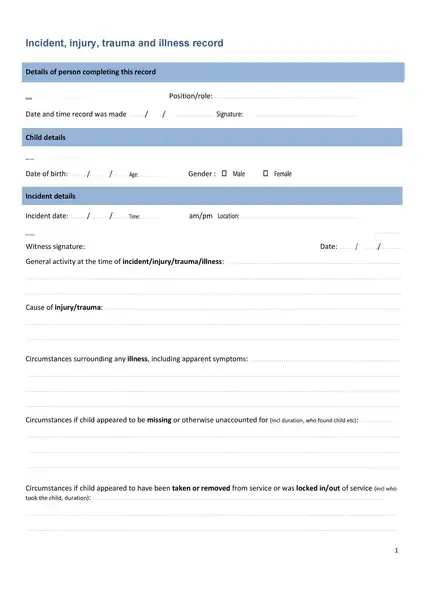

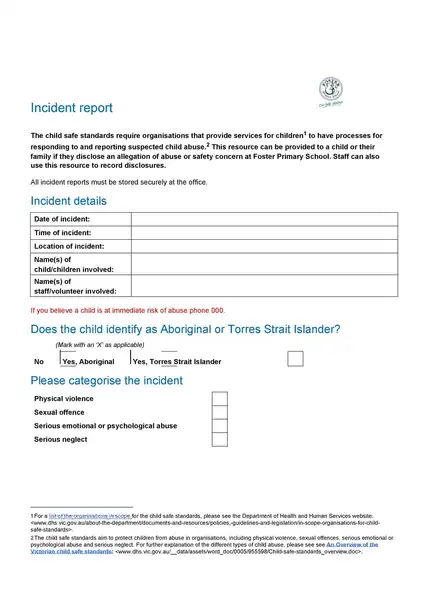
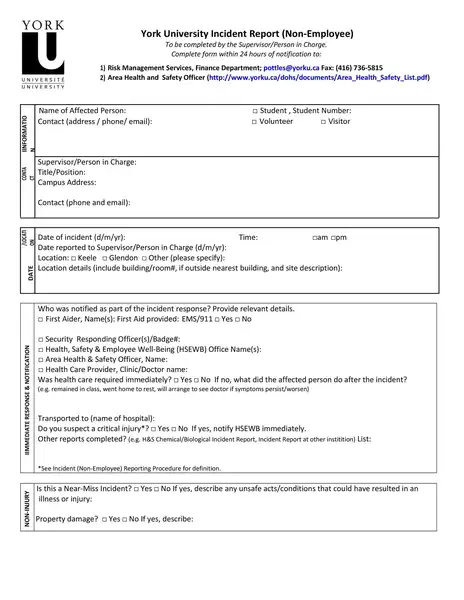
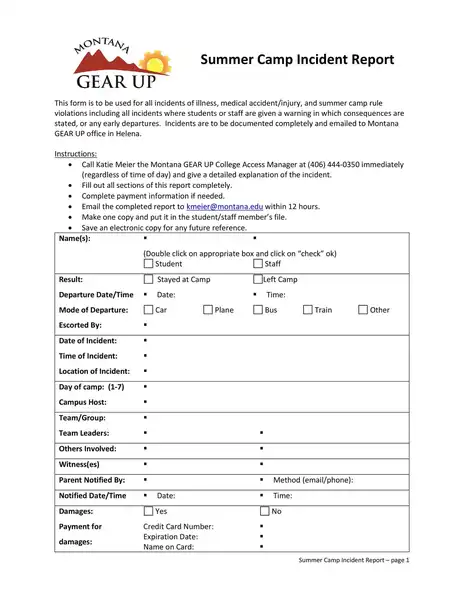
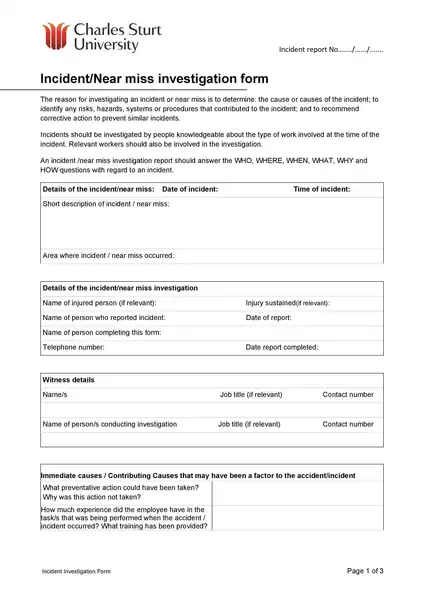





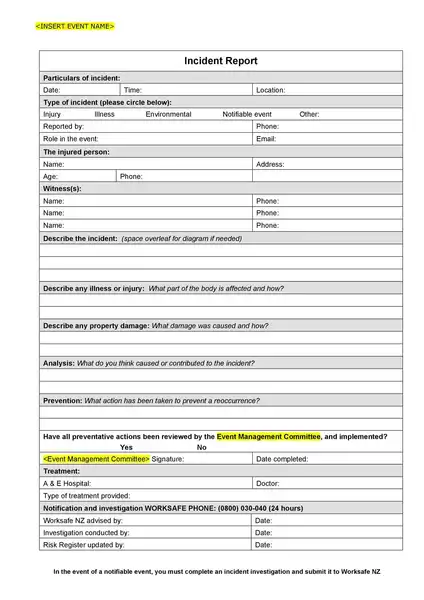
Whether you’re a small business owner, a safety officer in a large corporation, or a team leader in a community association, using an incident report template can create additional straightforwardness and effectiveness.
The goal is not just to document what happened but to understand why and how similar incidents can be prevented.
Tips for Effective Incident Reporting
Here are some helpful tips and best practices:
- Gather Precise Details: Ensure all facts related to the incident, such as date, time, location, and involved parties, are accurately documented.
- Stay Objective: Keep personal opinions and assumptions out of the report. Stick to the facts.
- Prompt Reporting: Report incidents as soon as possible to prevent the loss of crucial information and facilitate the investigation.
- Clear Language: Use straightforward, concise language for easy comprehension. Avoid jargon.
- Review Before Submission: Check the report for completeness and accuracy before submitting it.
Remember, timely and accurate incident reporting is key to workplace safety, legal compliance, and the organization’s and its employees’ protection.
Legal Implications
Understanding the legal aspects is crucial for any organization. Here’s why:
- Legal Requirement: In many jurisdictions, reporting certain incidents is legal. Failure to report can result in fines, penalties, and other legal consequences.
- Evidence in Legal Proceedings: It can serve as evidence in legal proceedings. It can help establish what happened during an incident and who was involved.
- Protects the Organization: Proper reporting can protect the organization from potential lawsuits. It shows that the organization took the incident seriously and took steps to address it.
- Protects Employees: For employees, It can provide a record of workplace accidents or injuries, which can be crucial for workers’ compensation claims.
Organizations can ensure effective and compliant incident reporting by following the tips above and understanding the legal aspects.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions:
Why is it important to report minor incidents?
Even minor incidents can provide valuable insights into potential risks and hazards. By reporting these incidents, organizations can take preventive measures to avoid more serious incidents in the future.
What is the role of supervisors?
Supervisors play a crucial role . They are often the first to respond to an incident and are responsible for ensuring that the incident is properly reported and investigated.
How can we ensure effective incident reporting?
It can be ensured by training all employees, promoting a culture of safety and accountability, and using a standardized incident reporting system or template.
Case Studies
Real-life examples can provide valuable insights into the importance of incident reporting and how to handle incidents effectively. Here are a couple of examples:
A manufacturing company experienced a minor incident where a worker slipped but did not sustain any injuries. The incident was reported and investigated, leading to the discovery of a recurring spillage issue. The company addressed the problem, preventing future slips and potential injuries.
In a hospital setting, a nurse mistakenly administered the wrong medication to a patient. The incident was immediately reported, and the patient was closely monitored until the medication wore off. The incident report led to a review and update of the medication administration procedures, reducing the likelihood of similar errors in the future.
These case studies highlight the importance of incident reporting in identifying risks, improving safety procedures, and preventing future incidents. They also underscore the value of learning from mistakes and improving safety standards.

The content creator team at calipsotree.com is dedicated to making topics accessible to everyone, with over 9 years of experience in writing and breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand articles that answer readers’ financial questions.








